Magnetotactic bacteria: concepts, conundrums, and insights from a novel in situ approach using digital holographic microscopy (DHM)

Magnetotactic bacteria (MTB) are a diverse group of highly motile Gram-negative microorganisms with the common ability to orient along magnetic field lines, a behavior known as magnetotaxis. Ubiquitous in aquatic sediment environments, MTB are often microaerophilic and abundant at the oxic/anoxic interface. Magnetic field sensing is accomplished using intracellular, membrane-encased, iron-containing minerals known as magnetosomes. The chemistry, morphology and arrangement of magnetosomes differs substantially among different MTB. Although magnetic field sensing mechanisms, genetic bases and protein functions have been elucidated in select model organisms such as the Magnetospirillum strains and Desulfovibrio RS-1, not all findings are applicable to diverse clades of MTB. As the number of identified species has increased, it has become evident that many of the characteristics and mechanisms once presumed to be prototypical of MTB are in fact not universal. Here we present a general overview of the current state of MTB research for readers outside of the realm of prokaryotic research, focusing on recent discoveries, knowledge gaps and future directions. In addition, we report new insights acquired using holographic technology to observe and quantify microbial responses in magnetic fields that are earth-strength or weaker, providing a new ecophysiological approach to in situ MTB research.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save
Springer+ Basic
€32.70 /Month
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Buy Now
Price includes VAT (France)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
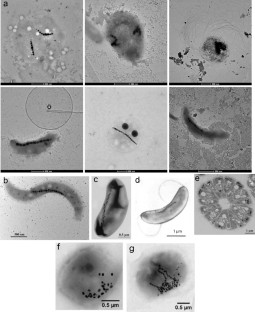
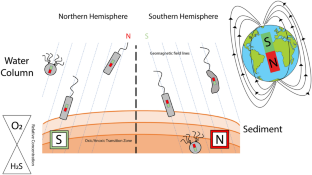
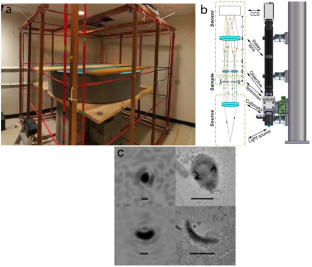
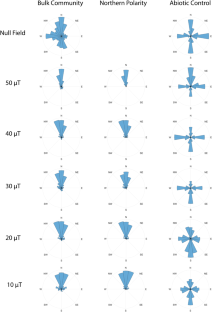
Similar content being viewed by others
Magnetotactic bacteria and magnetofossils: ecology, evolution and environmental implications
Article Open access 01 June 2022

Magnetotactic Bacteria
Chapter © 2013
Localized iron accumulation precedes nucleation and growth of magnetite crystals in magnetotactic bacteria
Article Open access 15 August 2017
Data availability
All data are available in the main text or the supplementary materials.
Code availability
References
- Abreu F, Cantão ME, Nicolás MF, Barcellos FG, Morillo V, Almeida LGP, do Nascimento FF, Lefèvre CT, Bazylinski DA, De Vasconcelos ATR, Lins U (2011) Common ancestry of iron oxide- and iron-sulfide-based biomineralization in magnetotactic bacteria. ISME J 5:1634–1640. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2011.35ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Alldred JC, Scollar I (1967) Square cross section coils for the production of uniform magnetic fields. J Sci Instrum 44:755–760. https://doi.org/10.1088/0950-7671/44/9/327ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Amor M, Tharaud M, Gélabert A, Komeili A (2020) Single-cell determination of iron content in magnetotactic bacteria: implications for the iron biogeochemical cycle. Environ Microbiol 22:823–831. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.14708ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Barber-Zucker S, Keren-Khadmy N, Zarivach R (2016) From invagination to navigation: the story of magnetosome-associated proteins in magnetotactic bacteria. Protein Sci 25:338–351. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.2827ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Baumgartner J, Morin G, Menguy N, Gonzalez TP, Widdrat M, Cosmidis J, Faivre D (2013) Magnetotactic bacteria form magnetite from a phosphate-rich ferric hydroxide via nanometric ferric (oxyhydr)oxide intermediates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:14883–14888. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1307119110ArticlePubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Bedrossian M, Barr CR, Lindensmith CA, Nealson KH, Nadeau JL (2017) Quantifying microorganisms at low concentrations using digital holographic microscopy (DHM). J vis Exp 129:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3791/56343ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Bellini S (2009) On a unique behavior of freshwater bacteria. Chinese J Oceanol Limnol 27:3–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-009-0003-5ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Bennet M, Bertinetti L, Neely RK, Schertel A, Körnig A, Flors C, Müller FD, Schüler D, Klumpp S, Faivre D (2015) Biologically controlled synthesis and assembly of magnetite nanoparticles. Faraday Discuss 181:71–83. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4fd00240gArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Biggin AJ, de Wit MJ, Langereis CG, Zegers TE, Voûte S, Dekkers MJ, Drost K (2011) Palaeomagnetism of Archaean rocks of the Onverwacht Group, Barberton Greenstone Belt (southern Africa): Evidence for a stable and potentially reversing geomagnetic field at ca. 3.5Ga. Earth Planet Sci Lett 302:314–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2010.12.024ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Blakemore RP (1982) Magnetotactic bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 36:217–238. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.001245ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Blakemore RP, Maratea D, Wolfe RS (1979) Isolation and pure culture of a freshwater magnetic spirillum in chemically defined medium. J Bacteriol 140:720–729. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.140.2.720-729.1979ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Chen H, Zhang SD, Chen L, Cai Y, Zhang WJ, Song T, Wu LF (2018) Efficient genome editing of Magnetospirillum magneticum AMB-1 by CRISPR-Cas9 system for analyzing magnetotactic behavior. Front Microbiol 9:1569. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01569ArticlePubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Cox BL, Popa R, Bazylinski DA, Lanoil B, Douglas S, Belz A, Engler DL, Nealson KH (2002) Organization and elemental analysis of P-, S-, and Fe-rich inclusions in a population of freshwater magnetococci. Geomicrobiol J 19:387–406. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490450290098504ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Dunin-Borkowski RE, McCartney MR, Frankel RB, Bazylinski DA, Posfai M, Buseck PR (1998) Magnetic microstructure of magnetotactic bacteria by electron holography. Science 282:1868–1870. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.282.5395.1868ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Faivre D, Böttger LH, Matzanke BF, Schüler D (2007) Intracellular magnetite biomineralization in bacteria proceeds by a distinct pathway involving membrane-bound ferritin and an iron(II) species. Angew Chemie - Int Ed 46:8495–8499. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200700927ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Faivre D, Menguy N, Pósfai M, Schüler D (2008) Environmental parameters affect the physical properties of fast-growing magnetosomes. Am Mineral 93:463–469. https://doi.org/10.2138/am.2008.2678ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Frankel RB, Bazylinski DA (2009) Magnetosomes and magneto-aerotaxis. Contrib Microbiol 16:182–193. https://doi.org/10.1159/000219380ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Frankel RB, Blakemore RP, Torres de Araujo FF, Esquivel DMS, Danon J (1981) Magnetotactic bacteria at the geomagnetic equator. Science 212:1269–1270. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.212.4500.1269ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Frankel RB, Papaefthymiou GC, Blakemore RP, O’Brien W (1983) Fe3O4 precipitation in magnetotactic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta - Mol Cell Res 763:147–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-4889(83)90038-1ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Garber AI, Nealson KH, Okamoto A, McAllister SM, Chan CS, Barco RA, Merino N (2020) FeGenie: a comprehensive tool for the identification of iron genes and iron gene neighborhoods in genome and metagenome assemblies. Front Microbiol 11:1–23. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.00037ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Jogler C, Niebler M, Lin W, Kube M, Wanner G, Kolinko S, Stief P, Beck AJ, de Beer D, Petersen N, Pan Y, Amann R, Reinhardt R, Schüler D (2010) Cultivation-independent characterization of “Candidatus Magnetobacterium bavaricum” via ultrastructural, geochemical, ecological and metagenomic methods. Environ Microbiol 12:2466–2478. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02220.xArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kasama T, Pósfai M, Chong RKK, Finlayson AP, Buseck PR, Frankel RB, Dunin-Borkowski RE (2006) Magnetic properties, microstructure, composition, and morphology of greigite nanocrystals in magnetotactic bacteria from electron holography and tomography. Am Mineral 91:1216–1229. https://doi.org/10.2138/am.2006.2227ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Kirschvink JL (1982) Paleomagnetic evidence for fossil biogenic magnetite in western Crete. Earth Planet Sci Lett 59:388–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-821X(82)90140-6ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Kolinko S, Jogler C, Katzmann E, Wanner G, Peplies J, Schüler D (2012) Single-cell analysis reveals a novel uncultivated magnetotactic bacterium within the candidate division OP3. Environ Microbiol 14:1709–1721. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02609.xArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kolinko S, Wanner G, Katzmann E, Kiemer F, FuchsSchüler MBD (2013) Clone libraries and single cell genome amplification reveal extended diversity of uncultivated magnetotactic bacteria from marine and freshwater environments. Environ Microbiol 15:1290–1301. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.12004ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kolinko I, Lohße A, Borg S, Raschdorf O, Jogler C, Tu Q, Pósfai M, Tompa É, Plitzko JM, Brachmann A, Wanner G, Müller R, Zhang Y, Schüler D (2014) Biosynthesis of magnetic nanostructures in a foreign organism by transfer of bacterial magnetosome gene clusters. Nat Nanotechnol 9:193–197. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2014.13ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kolinko S, Richter M, Glöckner FO, Brachmann A, Schüler D (2016) Single-cell genomics of uncultivated deep-branching magnetotactic bacteria reveals a conserved set of magnetosome genes. Environ Microbiol 18:21–37. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.12907ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Komeili A (2012) Molecular mechanisms of compartmentalization and biomineralization in magnetotactic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 36:232–255. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00315.xArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kopp RE, Kirschvink JL (2008) The identification and biogeochemical interpretation of fossil magnetotactic bacteria. Earth-Science Rev 86:42–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2007.08.001ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Koziaeva V, Dziuba M, Leão P, Uzun M, Krutkina M, Grouzdev D (2019) Genome-based metabolic reconstruction of a novel uncultivated freshwater magnetotactic coccus “Ca. Magnetaquicoccus inordinatus” UR-1, and proposal of a candidate family “Ca. Magnetaquicoccaceae”. Front Microbiol 10:1–20. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02290ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Kühn J, Niraula B, Liewer K, Kent WJ, Serabyn E, Graff E, Lindensmith C, Nadeau JL (2014) A Mach-Zender digital holographic microscope with sub-micrometer resolution for imaging and tracking of marine micro-organisms. Rev Sci Instrum 85:123113. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4904449ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Le Nagard L, Zhu X, Yuan H, Benzerara K, Bazylinski DA, Fradin C, Besson A, Swaraj S, Stanescu S, Belkhou R, Hitchcock AP (2019) Magnetite magnetosome biomineralization in Magnetospirillum magneticum strain AMB-1: a time course study. Chem Geol 530:119348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.119348ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Lefèvre CT, Bazylinski DA (2013) Ecology, diversity, and evolution of magnetotactic bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 77:497–526. https://doi.org/10.1128/mmbr.00021-13ArticlePubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Lefèvre CT, Frankel RB, Pósfai M, Prozorov T, Bazylinski DA (2011a) Isolation of obligately Alkaliphilic magnetotactic bacteria from extremely alkaline environments. Environ Microbiol 13:2342–2350. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02505.xArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lefèvre CT, Menguy N, Abreu F, Lins U, Pósfai M, Prozorov T, Pignol D, Frankel RB, Bazylinski DA (2011b) A cultured greigite-producing magnetotactic bacterium in a novel group of sulfate-reducing bacteria. Science 334:1720–1723. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1212596ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lefèvre CT, Trubitsyn D, Abreu F, Kolinko S, Jogler C, de Almeida LGP, de Vasconcelos ATR, Kube M, Reinhardt R, Lins U, Pignol D, Schüler D, Bazylinski DA, Ginet N (2013) Comparative genomic analysis of magnetotactic bacteria from the Deltaproteobacteria provides new insights into magnetite and greigite magnetosome genes required for magnetotaxis. Environ Microbiol 15:2712–2735. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.12128ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lefèvre CT, Bennet M, Landau L, Vach P, Pignol D, Bazylinski DA, Frankel RB, Klumpp S, Faivre D (2014) Diversity of magneto-aerotactic behaviors and oxygen sensing mechanisms in cultured magnetotactic bacteria. Biophys J 107:527–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2014.05.043ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Li Y (2021) Redox control of magnetosome biomineralization. J Oceanol Limnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-021-0422-5ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Li J, Zhang H, Menguy N, Benzerara K, Wang F, Lin X, Chen Z, Pan Y (2017) Single-cell resolution of uncultured magnetotactic bacteria via fluorescence-coupled electron microscopy. Appl Environ Microbiol 83:e00409-e417. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00409-17ArticlePubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Li J, Menguy N, Leroy E, Roberts AP, Liu P, Pan Y (2020) Biomineralization and magnetism of uncultured magnetotactic coccus strain THC-1 with non-chained magnetosomal magnetite nanoparticles. J Geophys Res Solid Earth. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020JB020853ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Lin W, Wang Y, Gorby Y, Nealson K, Pan Y (2013) Integrating niche-based process and spatial process in biogeography of magnetotactic bacteria. Sci Rep 3:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep01643ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Lin W, Deng A, Wang Z, Li Y, Wen T, Wu LF, Wu M, Pan Y (2014) Genomic insights into the uncultured genus “Candidatus Magnetobacterium” in the phylum Nitrospirae. ISME J 8:2463–2477. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2014.94ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Lin W, Pan Y, Bazylinski DA (2017a) Diversity and ecology of and biomineralization by magnetotactic bacteria. Environ Microbiol Rep 9:345–356. https://doi.org/10.1111/1758-2229.125504ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lin W, Paterson GA, Zhu Q, Wang Y, Kopylova E, Li Y, Knight R, Bazylinski DA, Zhu R, Kirschvink JL, Pan Y (2017b) Origin of microbial biomineralization and magnetotaxis during the Archean. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114:2171–2176. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1614654114ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Lin W, Zhang W, Zhao X, Roberts AP, Paterson GA, Bazylinski DA, Pan Y (2018) Genomic expansion of magnetotactic bacteria reveals an early common origin of magnetotaxis with lineage-specific evolution. ISME J 12:1508–1519. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-018-0098-9ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Lindensmith CA, Rider S, Bedrossian M, Wallace JK, Serabyn E, Showalter GM, Deming JW, Nadeau JL (2016) A submersible, off-axis holographic microscope for detection of microbial motility and morphology in aqueous and icy environments. PLoS ONE 11:e0147700. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0147700ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Liu P, Liu Y, Zhao X, Roberts AP, Zhang H, Zheng Y, Wang F, Wang L, Menguy N, Pan Y, Li J (2021) Diverse phylogeny and morphology of magnetite biomineralized by Magnetotactic cocci. Environ Microbiol 23:1115–1129. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.15254ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- McCausland HC, Komeili A (2020) Magnetic genes: studying the genetics of biomineralization in magnetotactic bacteria. PLoS Genet 16:e1008499. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1008499ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Nadeau J, Bin CY, El-Kholy M, Bedrossian M, Rider S, Lindensmith C, Wallace JK (2016) Holographic microscopy for 3D tracking of bacteria. Proc SPIE 9718:97182B. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2213021ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Philippe N, Wu LF (2010) An MCP-like protein interacts with the MamK cytoskeleton and is involved in magnetotaxis in Magnetospirillum magneticum AMB-1. J Mol Biol 400:309–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2010.05.011ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Qian XX, Liu J, Menguy N, Ji Li, Alberto F, Teng Z, Xiao T, Zhang W, Wu LF (2019) Identification of novel species of marine magnetotactic bacteria affiliated with Nitrospirae phylum. Environ Microbiol Rep 11:330–337. https://doi.org/10.1111/1758-2229.12755ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rosenberg E, DeLong EF, Stackebrandt E, Lory S, Thompson F (2013) The prokaryotes, vol. I, 4th edn. Springer, Berlin. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-30123-0BookGoogle Scholar
- Schindelin J, Arganda-Carreras I, Frise E, Kaynig V, Longair M, Pietzsch T, Preibisch S, Rueden C, Saalfeld S, Schmid B, Tinevez JY, White DJ, Hartenstein V, Eliceiri K, Tomancak P, Cardona A (2012) Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat Methods 9:676–682. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2019ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Simmons SL, Bazylinski DA, Edwards KJ (2006) South-seeking magnetotactic bacteria in the Northern Hemisphere. Science 311:371–374. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1122843ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Smalley MD, Marinov GK, Bertani LE, DeSalvo G (2016) Genome sequence of Magnetospirillum magnetotacticum strain MS-1. Genome Announc 3:1–2. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00233-15ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Uebe R, Schüler D (2016) Magnetosome biogenesis in magnetotactic bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol 14:621–637. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro.2016.99ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ullrich S, Kube M, Schübbe S, Reinhardt R, Schüler D (2005) A hypervariable 130-kilobase genomic region of Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense comprises a magnetosome island which undergoes frequent rearrangements during stationary growth. Microbiology 187:7176–7184. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.187.21.7176-7184.2005ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Uzun M, Alekseeva L, Krutkina M, Koziaeva V, Grouzdev D (2020) Unravelling the diversity of Magnetotactic bacteria through analysis of open genomic databases. Sci Data 7:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-020-00593-0ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Vali H, Kirschvink JL (1991) Observations of magnetosome organization, surface structure, and iron biomineralization of undescribed magnetic bacteria: evolutionary speculations. In: Frankel RB, Blakemore RP (eds) Iron biominerals. Springer, Boston Google Scholar
- Waite DW, Chuvochina M, Pelikan C, Parks DH, Yilmaz P, Wagner M, Loy A, Naganuma T, Nakai R, Whitman WB, Hahn MW, Kuever J, Hugenholtz P (2020) Proposal to reclassify the proteobacterial classes deltaproteobacteria and oligoflexia, and the phylum thermodesulfobacteria into four phyla reflecting major functional capabilities. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 70:5972–6016. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.004213ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wang X, Li Y, Zhao J, Yao H, Chu S, Song Z, He Z, Zhang W (2020) Magnetotactic bacteria: characteristics and environmental applications. Front Environ Sci Eng 14:56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-020-1235-zArticleCASGoogle Scholar
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Radu Popa, Tingting Yang and Leila Mahrokh for assistance in obtaining magnetotactic bacteria and TEM expertise. We also would like to thank the staff of the Los Angeles County Arboretum for their help and support in our research.
Funding
This work was funded in part by grants from the Air Force Office of Scientific Research to KHN, [FA9550-14-1-0208 and FA9550-20-1-0399 to K.J.L.], and the National Science Foundation [IOS-1456923 to K.J.L.].
Author information
- Casey R. Barr and Manuel Bedrossian have contributed equally to this work.
Authors and Affiliations
- Department of Earth Sciences, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, USA Casey R. Barr & Kenneth H. Nealson
- Department of Medical Engineering, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, USA Manuel Bedrossian
- Department of Biology, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, USA Kenneth J. Lohmann
- Department of Biological Sciences, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, USA Kenneth H. Nealson
- Casey R. Barr










